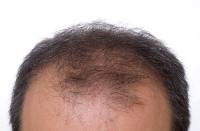
What causes male hair loss? There are many answers to this question, but in truth only a doctor can make a concrete determination. First, medical causes like thyroid imbalance, lupus, diabetes, liver disease and kidney disease must be ruled out. This necessarily involves traditional medical tests prescribed and evaluated by a physician. Your male hair loss, if it has an underlying medical cause like thyroid imbalance, can be treated and possibly reversed.
Your doctor may diagnose you with androgenic alopecia or alopecia areata as causes of your male hair loss. Androgenic alopecia is commonly known as male pattern baldness and occurs as the result of a complex set of genetic, hormonal and enzymatic interactions. Alopecia areata is thought to be an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system destroys body tissues (like hair) that it normally would ignore. Alopecia areata is treated with medium to very high potency topical corticosteriods, subcutaneous steroid injections and ultraviolet light.
Click Here For More Male Hair Loss Info And Tips!
Androgenic alopecia is by far the most common cause of male hair loss. Hair begins to thin at the temples, frontal hairline and crown. Over time hair will be completely lost in these areas, resulting in a fringe of hair remaining at the sides and back of the head only. The process of androgenic alopecia is thought to be genetically linked, that is, the follicles in the areas of the head experiencing balding are inherit a sensitivity to the action of a hormone called DHT or dihydrotestosterone. DHT is formed when the hormone testosterone is converted via the action of an enzyme named 5-alpha reductase.
An overabundance of DHT in a man’s body causes the DHT that is present in the scalp to attack follicles that are genetically predisposed to be sensitive to it. DHT works to make the follicle miniaturize, with the result that the hairs produced become thinner and thinner. Eventually the hair becomes transparent and the follicle becomes inactive — it stops producing hair. Note that only susceptible follicles are affected. The hair at the sides and back of the head is naturally resistant to the action of DHT — an important fact to know when considering treatments for male hair loss. This resistant hair can be transplanted to balding areas to recreate your hairline.
Treatments for androgenic alopecia include drugs that block the action of DHT. These drugs may be combined with growth stimulators that cause the follicle to produce hair despite the action of DHT. The best-known DHT blocker is the prescription drug PropeciaÒ, generic name finasteride. Finasteride actually works to block the action of the 5-alpha reductase enzyme that is responsible for turning testosterone into DHT. In a clinical study, 64% of patients who took this drug for male hair loss experienced hair regrowth after to 2 years. The drug is even more effective in helping you keep the hair you have.
The most familiar growth stimulant is a non-prescription topically applied product named RogaineÒ, generic name minoxidil. In a clinical study, 59% of male hair loss sufferers began regrowing hair within 4 months. Minoxidil may also be a good preventative.
The best regimen is a combination of finasteride and minoxidil as a treatment for male hair loss caused by androgenic alopecia. See your doctor first. If you have androgenic alopecia, there are potent medicines to help you combat it.